Indentation Modulus
| A service provided by |
|---|

|
| Polymer Service GmbH Merseburg |
| Tel.: +49 3461 30889-50 E-Mail: info@psm-merseburg.de Web: https://www.psm-merseburg.de |
| Our further education offers: https://www.psm-merseburg.de/weiterbildung |
| PSM on Wikipedia: https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polymer Service Merseburg |
Indentation modulus
Definition of the indentation modulus
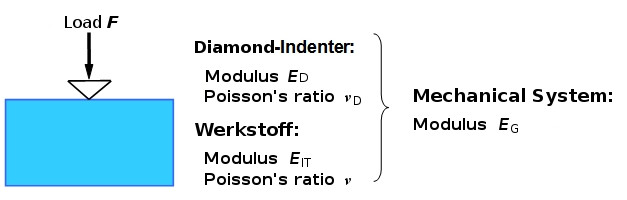
The indentation modulus EIT (in MPa) is determined in the micro load range of the hardness test using a method described in detail in ISO 14577 [1] from the initial rise of the unloading curve of the load (F)–indentation depth (h) diagram (see: instrumented hardness testing – method & material parameters) at the maximum load Fmax (dF/dh|Fmax). In the nanolast range of hardness testing, the method according to Oliver and Pharr is usually used [2]. According to ISO 14577, it is taken into account that the mechanical resistances of the test specimen and diamond indenter are connected in parallel (see Figure and Eq. 1)
| (1) |
This results in EIT:
| (2) |
from which the following expression can be derived using the relationships described in detail in ISO 14577:
| (3) |
The Poisson's ratio required to calculate EIT is known for most materials and is relatively independent of temperature. The value 8.73 x 10-13 Pa-1 is the effective compliance of diamond.
Application limits
When using the indentation modulus EIT, it is important to note that although EIT is fundamentally equivalent to a modulus of elasticity, it only describes the stiffness behaviour very locally and under triaxial loading. This results in a difference in value to the characteristic values of the modulus of elasticity, which were determined using conventional plastic testing methods, such as the uniaxial tensile or compression test or the three- or four-point bending test. The indentation modulus can therefore not be used for dimensioning purposes.
See also
- Elastic modulus
- Instrumented hardness testing – method & material parameters
- vickers hardness
- Ultrasound – elastic parameters
- Indentation fracture mechanics
References
| [1] | ISO 14577: Metallic Materials – Instrumented Indentation Test for Hardness and Materials Parameters
|
| [2] | Oliver, W. C., Pharr, G. M.: An Improved Technique for Determining Hardness and Elastic Modulus using Load and Displacement Sensing Indentation. J. of Materials Research 7 (1992) 1564–1583 |