CT-Specimen: Difference between revisions
Oluschinski (talk | contribs) Created page with "{{Language_sel|LANG=ger|ARTIKEL=Kompaktzugprüfkörper}} {{PSM_Infobox}} <span style="font-size:1.2em;font-weight:bold;">Compact tension specimen</span> __FORCETOC__ The term ‘compact tension specimen’ or also `compact tensile test specimen` can be found in many German-language (usually somewhat older) publications. Today, the term ‘CT test specimen’ or ‘CT-specimen’ has become widely accepted, i.e. in German-language and Anglo-Saxon literatur..." |
Oluschinski (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Language_sel|LANG=ger|ARTIKEL= | {{Language_sel|LANG=ger|ARTIKEL=CT-Prüfkörper}} | ||
{{PSM_Infobox}} | {{PSM_Infobox}} | ||
<span style="font-size:1.2em;font-weight:bold;">Compact tension specimen</span> | <span style="font-size:1.2em;font-weight:bold;">CT-specimen or written in full Compact tension (CT) specimen</span><br><br> | ||
The Anglo-Saxon abbreviation CT stands for ‘Compact Tension’ and the CT-test specimen is referred to in German as a compact tensile test specimen. | |||
__FORCETOC__ | __FORCETOC__ | ||
''' | ==Requirements for test specimen geometry== | ||
When experimentally determining fracture mechanical values (see: [[Fracture Mechanical Testing|fracture mechanical testing]]), the following basic conditions must be observed: | |||
# Under the respective test conditions, the test specimen dimensions must be significantly larger than the extent of the [[Plastic Zone|plastic zone]] at the [[Crack|crack tip]]. | |||
# The force, notch expansion (see: [[Crack Opening|crack opening]]) and load-load application point displacement must be continuously measurable. | |||
# To calculate the [[Fracture Mechanics|stress intensity factor]] ''K'' at the moment of unstable [[Crack Propagation|crack propagation]], the stress on the test [[Specimen|specimen]] and the critical crack length must be precisely determinable. | |||
# For the corresponding test specimen geometry, the determining equation, i.e. the relationship between [[Stress|stress]] and [[Initial Crack Length|crack length]], must be known. | |||
In order to fulfill these requirements, a series of specifications were established based on ASTM standard E 399 [1] and incorporated into the existing standards. | |||
==Test specimen shape== | |||
[[File:CT-Specimen.jpg|500px]] | |||
{| | |||
|- valign="top" | |||
|width="50px"|'''Fig.''': | |||
|width="600px" |Schematic illustration of the CT-specimen | |||
|} | |||
'''Dimension (according [1, 2]):''' | |||
<br> | |||
''W'' = 2 B, special shape: ''W'' = ''B'' to 4 ''B'' | |||
<br> | |||
''s'' = 0.55 | |||
<br> | |||
''H'' = 1.2 W | |||
<br> | |||
''a'' = (0.35–0.55) ''W'' | |||
<br> | |||
''D'' = 0.25 ''W'' | |||
<br> | |||
''G'' = 1.25 ''W'' | |||
'''Typical dimensions for plastics [3. 4]:''' | |||
<br> | |||
Example 1: Designation: ''48 mm x 50 mm-specimen'' | |||
<br> | |||
''W'' = 40 mm, ''B'' = 10 mm, ''H'' = 48 mm, ''G'' = 50 mm, ''D'' = 10 mm, ''L'' = 12 mm, ''a'' = 18 mm, ''s'' = 22 mm, ''N'' = 2 mm | |||
<br><br> | |||
Example 2: Designation: ''96 mm x 100 mm-specimen'' | |||
<br> | |||
''W'' = 80 mm, ''B'' = 3...10 mm, ''H'' = 96 mm, ''G'' = 100 mm, ''D'' = 20 mm, ''L'' = 36 mm, ''a'' = 38 mm, ''s'' = 44 mm, ''l'' = 2 mm | |||
<br> | |||
==Determination equation [1]== | |||
{| | |||
|- | |||
|width="20px"| | |||
|width="500px" | <math>K_I = \frac{F}{B \cdot W^{1/2}} f(a/W)</math> | |||
|} | |||
{| | |||
|- | |||
|width="20px"| | |||
|width="500px" | <math>f(a/W) = 29.6(a/W)^{1/2}-185.5(a/W)^{3/2}+655.7(a/W)^{5/2}-1017(a/W)^{7/2}+638.9(a/W)^{9/2} \!\ </math> | |||
|} | |||
Designation according thickness ''B'': | |||
<br> | |||
CT 10, CT 15, CT 20, CT 30 | |||
'''Geometry criterion for metals:''' | |||
{| | |||
|- | |||
|width="20px"| | |||
|width="500px" | <math>B, a, (W-a) \geq 2.5 \bigg(\frac {K_I}{R_e}\bigg)^2</math> | |||
|} | |||
'''Geometry criterion for plastics:''' | |||
{| | |||
|- | |||
|width="20px"| | |||
|width="500px" | <math>B, a, (W-a) \geq \beta \bigg(\frac {K}{\sigma_y}\bigg)^2</math> | |||
|} | |||
It is valid: ''R''<sub>e</sub> = ''y'' = [[Yield Stress|Yield stress]] (yield point) | |||
The geometry constant ''β'' depends on the material (see also: [[Geometry Criterion|geometry criterion]], [[Fracture Mechanics|fracture toughness]]). | |||
A comprehensive summary of suitable test specimens for [[Fracture Mechanical Testing|fracture mechanics investigations]] on [[Plastics|plastics]] and [[Composite Materials Testing|composite materials]] is included in [[Specimen for Fracture Mechanics|fracture mechanics test specimens]]. | |||
==See also== | |||
* [[ | * [[Specimen for Fracture Mechanics|Specimen for fracture mechanics tests]] | ||
* [[ | * Compact tension specimen | ||
* [[ | * [[Geometry Function|Geometry function]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Laser Double-Scanner|Laser double-scanner]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Hybrid Methods, Examples|Hybrid methods, examples]] | ||
* [[Laser Multi-Scanner|Laser multi-scanner]] | |||
* [[Toughness Temperature Dependence|Toughness temperature dependence]] | |||
'''References''' | '''References''' | ||
{| | |||
|-valign="top" | |||
|[1] | |||
|ASTM E 399 (2024): Standard Test Method for Linear-Elastic Plane-Strain Fracture Toughness of Metallic Materials | |||
|-valign="top" | |||
|[2] | |||
|[[Blumenauer, Horst|Blumenauer, H.]], Pusch, G.: Technische Bruchmechanik. Deutscher Verlag für Grundstoffindustrie, Leipzig Stuttgart (1993) 3rd Edition, (ISBN 3-342-00659-5; see [[AMK-Büchersammlung|AMK-Library]] under E 29-3) | |||
|-valign="top" | |||
|[3] | |||
|[[Grellmann, Wolfgang|Grellmann, W.]], [[Seidler, Sabine|Seidler, S.]] (Eds.): Deformation and Fracture Behaviour of Polymers. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg (2001) (ISBN 978-3-540-41247-6; e-Book: ISBN 978-3-662-04556-5; see [[AMK-Büchersammlung|AMK-Library]] under A 7) | |||
|-valign="top" | |||
|[4] | |||
|[https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Wolfgang-Grellmann Grellmann, W.], [https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sabine_Seidler Seidler, S.] (Eds.): Polymer Testing. Carl Hanser, Munich (2022) 3rd Edition, pp. 233/234 (ISBN 978-1-56990-806-8; E-Book: ISBN 978-1-56990-807-5; see [[AMK-Büchersammlung|AMK-Library]] under A 22) | |||
|} | |||
[[Category:Fracture Mechanics]] | |||
[[Category:Specimen]] | [[Category:Specimen]] | ||
Latest revision as of 06:51, 15 December 2025
| A service provided by |
|---|

|
| Polymer Service GmbH Merseburg |
| Tel.: +49 3461 30889-50 E-Mail: info@psm-merseburg.de Web: https://www.psm-merseburg.de |
| Our further education offers: https://www.psm-merseburg.de/weiterbildung |
| PSM on Wikipedia: https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polymer Service Merseburg |
CT-specimen or written in full Compact tension (CT) specimen
The Anglo-Saxon abbreviation CT stands for ‘Compact Tension’ and the CT-test specimen is referred to in German as a compact tensile test specimen.
Requirements for test specimen geometry
When experimentally determining fracture mechanical values (see: fracture mechanical testing), the following basic conditions must be observed:
- Under the respective test conditions, the test specimen dimensions must be significantly larger than the extent of the plastic zone at the crack tip.
- The force, notch expansion (see: crack opening) and load-load application point displacement must be continuously measurable.
- To calculate the stress intensity factor K at the moment of unstable crack propagation, the stress on the test specimen and the critical crack length must be precisely determinable.
- For the corresponding test specimen geometry, the determining equation, i.e. the relationship between stress and crack length, must be known.
In order to fulfill these requirements, a series of specifications were established based on ASTM standard E 399 [1] and incorporated into the existing standards.
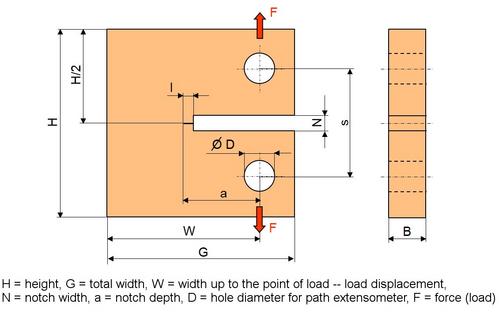
Test specimen shape
| Fig.: | Schematic illustration of the CT-specimen |
Dimension (according [1, 2]):
W = 2 B, special shape: W = B to 4 B
s = 0.55
H = 1.2 W
a = (0.35–0.55) W
D = 0.25 W
G = 1.25 W
Typical dimensions for plastics [3. 4]:
Example 1: Designation: 48 mm x 50 mm-specimen
W = 40 mm, B = 10 mm, H = 48 mm, G = 50 mm, D = 10 mm, L = 12 mm, a = 18 mm, s = 22 mm, N = 2 mm
Example 2: Designation: 96 mm x 100 mm-specimen
W = 80 mm, B = 3...10 mm, H = 96 mm, G = 100 mm, D = 20 mm, L = 36 mm, a = 38 mm, s = 44 mm, l = 2 mm
Determination equation [1]
Designation according thickness B:
CT 10, CT 15, CT 20, CT 30
Geometry criterion for metals:
Geometry criterion for plastics:
It is valid: Re = y = Yield stress (yield point)
The geometry constant β depends on the material (see also: geometry criterion, fracture toughness).
A comprehensive summary of suitable test specimens for fracture mechanics investigations on plastics and composite materials is included in fracture mechanics test specimens.
See also
- Specimen for fracture mechanics tests
- Compact tension specimen
- Geometry function
- Laser double-scanner
- Hybrid methods, examples
- Laser multi-scanner
- Toughness temperature dependence
References
| [1] | ASTM E 399 (2024): Standard Test Method for Linear-Elastic Plane-Strain Fracture Toughness of Metallic Materials |
| [2] | Blumenauer, H., Pusch, G.: Technische Bruchmechanik. Deutscher Verlag für Grundstoffindustrie, Leipzig Stuttgart (1993) 3rd Edition, (ISBN 3-342-00659-5; see AMK-Library under E 29-3) |
| [3] | Grellmann, W., Seidler, S. (Eds.): Deformation and Fracture Behaviour of Polymers. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg (2001) (ISBN 978-3-540-41247-6; e-Book: ISBN 978-3-662-04556-5; see AMK-Library under A 7) |
| [4] | Grellmann, W., Seidler, S. (Eds.): Polymer Testing. Carl Hanser, Munich (2022) 3rd Edition, pp. 233/234 (ISBN 978-1-56990-806-8; E-Book: ISBN 978-1-56990-807-5; see AMK-Library under A 22) |