Sound Power
| A service provided by |
|---|

|
| Polymer Service GmbH Merseburg |
| Tel.: +49 3461 30889-50 E-Mail: info@psm-merseburg.de Web: https://www.psm-merseburg.de |
| Our further education offers: https://www.psm-merseburg.de/weiterbildung |
| PSM on Wikipedia: https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polymer Service Merseburg |
Sound power
Definition
Sound power is a material parameter that is widely used in non-destructive polymer testing, particularly in acoustic resonance analysis and ultrasound testing. It represents the sound energy emitted per unit of time, e.g. by a motor or machine, and is evaluated according to perception-oriented criteria and expressed as sound power level LP. Caution is advised when calculating with logarithmic values. Adding levels corresponds to multiplying the underlying linear measured values. Adding two sound levels of equal magnitude results in a sound level that is 3 dB higher.
| 1 dB | smallest audible level difference |
| 3 dB | doubling of power |
| 6 dB | doubling of amplitude, 4 times the power |
| 10 dB | doubling of subjective loudness, 10 times the power |
| 20 dB | ten times the amplitude, 100 times the power |
Reference
- Hertlin, Ingolf: Informationsschriften zur zerstörungsfreien Prüfung – ZfP kompakt und verständlich. Band 5: Akustische Resonanzanalyse. Castell Verlag GmbH, Wuppertal (2003)
Acoustic sound field variables
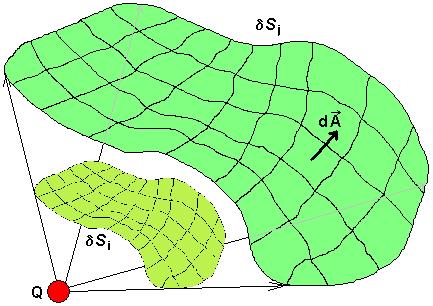
The sound power PS describes the energy that flows from a sound source Q through a closed surface area S surrounding it. It is the integral of the sound intensity IS over the closed surface area S.
The sound power is related to the sound intensity as follows:
Since sound intensity, which represents a flow of energy, is an energetic parameter, the surface around the sound source can be chosen arbitrarily. The figure shows two equivalent surface segments δS as an example, whose geometry is proportional to the distance from the sound source Q. Integrating over both surface segments would yield the same result.
| Figure: | Representation of arbitrarily curved surfaces through which the sound energy emitted by a sound source Q flows |
The sound power is determined in accordance with the envelope method specified in ISO 3744.
See also
References
- Stöcker, H.: Taschenbuch der Physik. Harri Deutsch Verlag, Frankfurt/Main (1994), (ISBN 978-3-8171-1720-8)
- Winkelmann, A. A.: Handbuch der Physik. 2nd Volume (Akustik) Barth (1909)
- Kuttruff, H.: Akustik – Eine Einführung. S. Hirzel Publishing, Stuttgart Leipzig (2004), (ISBN 3-7776-1244-8)
- v. Ardenne, M.: Effekte der Physik und ihre Anwendungen. Harri Deutsch Verlag, Frankfurt/Main (2005), (ISBN 978-3-8171-1682-9)
- ISO/FDIS 3744 (2024-07): Acoustics – Determination of Sound Power Levels of Noise Sources Using Sound Pressure – Engineering Methods for an Essentially Free Field over a Reflecting Plane (Draft)