Instrumented Scratch Testing: Difference between revisions
Oluschinski (talk | contribs) Created page with "{{Language_sel|LANG=ger|ARTIKEL=Instrumentierte Kratzprüfung}} {{PSM_Infobox}} <span style="font-size:1.2em;font-weight:bold;">Instrumented scratch testing or registering scratch test</span> __FORCETOC__ ==Recording scratch testing machines== Instrumented scratch testing is carried out using recording scratch testing machines ('''Fig. 1'''), which have three-dimensionally movable measuring tables in a horizontal or vertical arrangement and corresponding indenters (e.g..." |
(No difference)
|
Latest revision as of 10:46, 2 December 2025
| A service provided by |
|---|

|
| Polymer Service GmbH Merseburg |
| Tel.: +49 3461 30889-50 E-Mail: info@psm-merseburg.de Web: https://www.psm-merseburg.de |
| Our further education offers: https://www.psm-merseburg.de/weiterbildung |
| PSM on Wikipedia: https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polymer Service Merseburg |
Instrumented scratch testing or registering scratch test
Recording scratch testing machines
Instrumented scratch testing is carried out using recording scratch testing machines (Fig. 1), which have three-dimensionally movable measuring tables in a horizontal or vertical arrangement and corresponding indenters (e.g. Rockwell or Vickers indenters). These testing machines enable separate force and displacement measurement in the xyz or xz direction, whereby the test can be performed with penetration depth control, force control, penetration depth speed control or force speed control, depending on the testing machine, application and customer requirements (see also: tensile test control).
| Fig. 1: | Recording scratch testing machine from the company Coesfeld, a) General view b) Specimen table for film testing (vacuum table) |
Performing the scratch test
The instrumented scratch test is used for the multi-parameter evaluation of the scratch resistance of plastic surfaces of compact flat test specimens or components, coatings and paints on a substrate, as well as plastic films.
The measurement can be carried out in accordance with standards such as ISO 19252 or ASTM D 7027. However, these currently existing standards do not even begin to utilise the potential of the method, as they do not go beyond the exclusive evaluation of measured variables. However, efforts are currently being made to utilise the adjustable experimental parameters and the measurable variables directly for the reproducible determination of specific scratch properties, as shown in the Table 1 below. Only then can the full potential of the method be utilised, as has already been the case with the instrumented hardness test.
Measurement parameters of the scratch test
Table 1 contains a list of the experimental parameters of the measured variables and the scratch properties of the instrumented scratch test.
| Experimental parameter | Measurement variables | Scratch properties |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
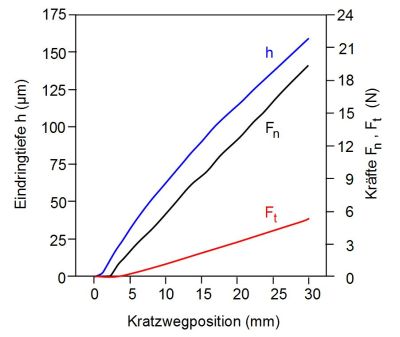
For this purpose, it is necessary to measure both the tangential load and the penetration depth as a function of time or the scratching path (Fig. 2) and to measure the scratch groove width microscopically.
| Fig. 2: | Load speed-controlled measurement on PVC using a recording scratch testing machine |
See also
- scratch resistance
- Scratch hardness
- Plastic films & Varnishes – Surface technology
- Instrumented hardness testing – Method & Material parameters
- Instrumented adhesion test
- Surface testing technology
References
- ISO 1518: Paints and Varnishes – Determination of Scratch Resistance –
- Part 1 (2023-05): Constant Loading Method
- Part 2 (2019-10): Variable-loading method
- ASTM D 7027 (2020): Standard Test Method for Evaluation of Scratch Resistance of Polymeric Coatings and Plastics Using an Instrumented Scratch Machine
- ISO 18922 (2003-05): Imaging Materials – Processed Photographic – Methods for Determining Scratch Resistance
- ISO 19252 (2025-05): Plastics – Determination of Scratch Properties
- Rybnicek, J., Lach, R., Dominguez, S. R., Tondl, D., Valek, R., Grellmann, W.: Kratzfestigkeit von PA6-Nanokompositen. GAK – Gummi Fasern Kunststoffe 65 (2012) 775–783 (https://www.researchgate.net/publication/235407233_Kratzfestigkeit_von_PA6-Nanokompositen)
- Reincke, K.: Testing of Polymeric Films. In: Grellmann, W., Seidler, S. (Eds.): Polymer Testing. Carl Hanser Munich (2022) 3rd. Edition, pp. 643–678 (ISBN 978-1-56990-806-8; e-Book ISBN 978-1-56990-807-5; ePub ISBN 978-1-56990-802-2; see AMK-Library under A 22)
Weblinks
- Wikipedia – The Free Encyclopedia: Mohs, Carl Friedrich Christian; https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Friedrich_Mohs