Crack Model according to DUGDALE: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Oluschinski (talk | contribs) Created page with "{{Language_sel|LANG=ger|ARTIKEL=Rissmodell nach DUGDALE}} {{PSM_Infobox}} <span style="font-size:1.2em;font-weight:bold;">Crack model according to DUGDALE</span> __FORCETOC__ ==Fundamentals of the concept== DUGDALE's crack model was derived by WELLS in 1961 and is considered the basis for the Crack tip opening displacement concept (CTOD) concept of yield fracture mechanics...." |
(No difference)
|
Latest revision as of 08:00, 1 December 2025
Sprachauswahl/Language selection
Dieser Artikel ist auch auf Deutsch verfügbar  Rissmodell nach DUGDALE
Rissmodell nach DUGDALE
| A service provided by |
|---|

|
| Polymer Service GmbH Merseburg |
| Tel.: +49 3461 30889-50 E-Mail: info@psm-merseburg.de Web: https://www.psm-merseburg.de |
| Our further education offers: https://www.psm-merseburg.de/weiterbildung |
| PSM on Wikipedia: https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polymer Service Merseburg |
Crack model according to DUGDALE
Fundamentals of the concept
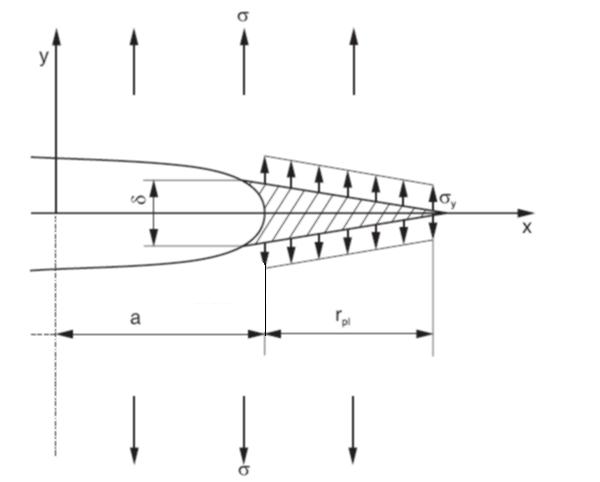
DUGDALE's crack model was derived by WELLS in 1961 and is considered the basis for the Crack tip opening displacement concept (CTOD) concept of yield fracture mechanics. It is based on the assumption that with ductile material behaviour, the fracture process is controlled by a critical plastic deformation, the crack tip opening displacement CTOD or crack opening δ.
| Fig.: | Crack model according to DUGDALE |
The formation of the plastic zone rpl depends on the microstructure and therefore cannot be represented in a generally valid form. Deviating from the modelling of the theoretical concepts of fracture mechanics, material-specific plastic zones are demonstrated experimentally.
See also
- Fracture mechanics
- Crack models
- Crack model according to BARENBLATT
- Crack model according to GRIFFITH
- Crack model according to IRWIN and Mc CLINTOCK
References
- Dugdale, D. S.: Yielding of Steel Sheets Containing Slits. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 8 (1960) 2, 100 – 104, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-5096(60)90013-2
- Blumenauer, H., Pusch, G.: Technische Bruchmechanik. Deutscher Verlag für Grundstoffindustrie, Leipzig Stuttgart (1993) 3. Auflage, S. 19, (ISBN 3-342-00659-5; siehe AMK-Büchersammlung unter E 29-3)
- Anderson, T. L.: Fracture Mechanics; Fundamentals and Applications. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2005) 3. Auflage, (ISBN 978-0849342608; siehe AMK-Büchersammlung unter E 8-2), DOI: https://doi.org/10.1201/9781315370293
- Grellmann, W., Seidler, S. (Eds.): Polymer Testing. Carl Hanser Munich (2022) 3. Edition, 236–239 (ISBN 978-1-56990-806-8; see under AMK-Library A 22) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/C2020-0-01638-5