Strain Gauge
| A service provided by |
|---|

|
| Polymer Service GmbH Merseburg |
| Tel.: +49 3461 30889-50 E-Mail: info@psm-merseburg.de Web: https://www.psm-merseburg.de |
| Our further education offers: https://www.psm-merseburg.de/weiterbildung |
| PSM on Wikipedia: https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polymer Service Merseburg |
Strain gauge
Areas of application for strain gauges (DMS)
Mechanical extensometers
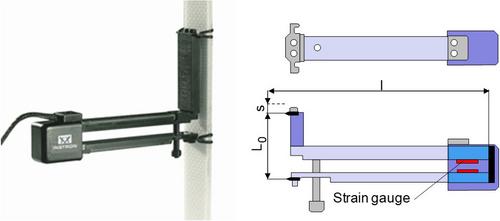
Strain gauges, often referred to as DMS in German-speaking countries, are used in measurement and testing technology for various tasks [1, 2]. One major area of use is in strain sensor technology, where particularly light and precise mechanical extensometers or strain sensors can be realised. Such extensometers can also be used in a wide temperature range (Fig. 1) [3].
| Fig. 1: | Functional principle of the mechanical extensometer Instron 2620-601 [3] |
If an extension ΔL is measured in the tensile test, this corresponds to an elastic deflection s at the measuring edges of the strain sensor, which can be described by the bending line below:
Electro-mechanical load cell
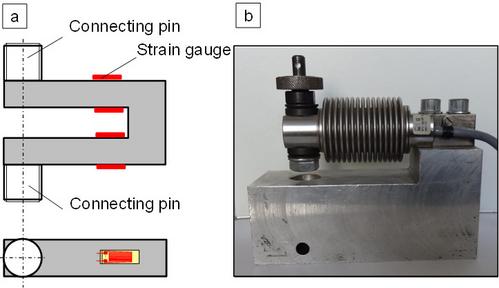
Another important area of application for DMS is in the use of electro-mechanical load cells, which are based on the elastic deformation measurement of a deformation body. If a stress is applied to this body in a tensile test or compression test, this deformation body is elastically compressed or stretched, causing a contraction or elongation of the strain gauge. The resulting change in resistance causes a change in stress, which is calibrated in units of force and used to indicate force or stress. When a load cell is subjected to a bending load (Fig. 2), the deflection can be calibrated in force units in the same way as with the strain sensor.
| Fig. 2: | Functional principle of a) an electro-mechanical load cell and b) 200 N load cell of company Zwick type Z6-3 (photo of company ZwickRoell |
Direct stress and strain measurement
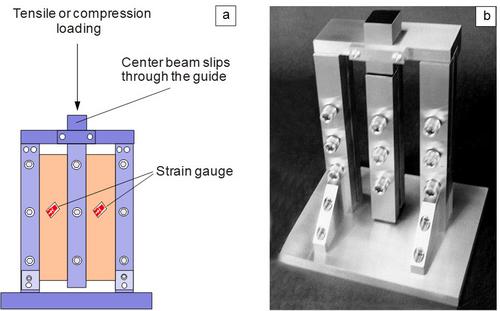
Strain gauges can also be used for direct strain measurement or stress measurement on the test specimen, although these are usually so-called ‘lost sensors’ as they are destroyed when the test specimen breaks. The DMS are mostly used in composite testing for off-axis tensile tests or, for example, for two- or three-rail shear tests (Fig. 3), where conventional extensometers cannot be applied.
| Fig. 3: | Schema a) and view of a three-rail shear testing device according to ASTM D 4255 b) [4] |
An important field of application is experimental stress analysis or strain analysis, which is used to assess complex multiaxial stress states and strain states and is also used in particular to verify FEM calculations. The mechanical stress or strain are important parameters for the evaluation of component stress. In addition to the use of field measurement techniques, the use of strain gauges offers a simple and reliable method of carrying out detailed analyses of the stress or strain state. This is particularly important when only insufficient or inaccurate information on the actual component stress is available. DMS can then be used to determine the real operating loads of a component during loading.
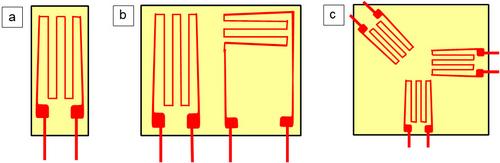
Using variable application techniques or special types of DMS, the normal stress components under tensile or compressive load, bending stresses (bending moment) or even acting torsional stresses or torques can be recorded separately, whereby specially assembled DMS rosettes with defined measuring grid directions are often used here (Fig. 4).
| Fig. 4: | Scheme of basic layouts of strain gauges a) one-, b) two- and three-dimensional (strain gauge rosette) |
Structure of strain gauges (DMS)
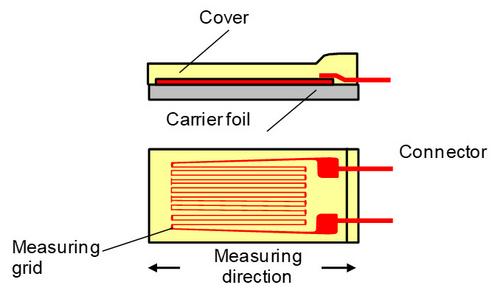
Strain gauges usually consist of a substrate film to which the respective measuring grid is applied, which is connected to contacts on the connection side. To protect the strain gauge, a capping compound is moulded on the top.
The application of DMS to a test or measurement object usually requires an ideal connection between the two parts using suitable adhesives that can ensure loss-free coupling [5]. The electrical connection is made via the soldering lugs, e.g. of the metal foil DMS, which is electrically integrated into a Wheatstone bridge. If the specific resistance of the DMS changes due to compression or strain, the symmetry of the bridge circuit changes (detuning of the bridge) and thus the bridge voltage (strain-resistance effect). Due to the low output voltage, a measuring amplifier must be connected downstream, which forms the actual measuring chain with the bridge and the DMS, which is connected to the display unit (PC or voltmeter).
| Fig. 5: | Schematically design of strain gauges |
Depending on the physical measuring principle, strain gauges are divided into metallic strain gauges or semiconductor strain gauges (HL-DMS) and thin-film strain gauges, which are vapour-deposited directly onto the object to be measured. Special forms, which are only of minor technical importance, are piezo-electric and voltage-optical strain gauges [5].
See also
- ICIT ( Instrumented Charpy impact test)
- MPK procedure "MPK-ICIT"
- ITIT (Instrumented Tensile-Impact Test) (see MPK-Procedure MPK-ITIT)
References
| [1] | Schrüfer, E., Reindl, M., Zagar, B.: Elektrische Messtechnik. Messung elektrischer und nichtelektrischer Größen. Carl Hanser, Munich (2022) 13. Auflage (ISBN: 978-3-446-47164-1) |
| [2] | Laible, M., Bill, B., Gehrke, K.: Mechanische Größen elektrisch gemessen–Grundlagen und Beispiele zur technischen Ausführung. Expert Verlag, Renningen (2013) 8. Auflage (ISBN: 978-3-8169-3215-4) |
| [3] | Instron Datenblatt: Extensometer 2620-601; https://www.instron.com/de-de/products/testing-accessories/extensometers/axial-clip-on/dynamic/2620-601 |
| [4] | Altstädt, V.: Testing of Composite Materials. In: Grellmann, W., Seidler, S. (Eds.): Polymer Testing. Carl Hanser, Munich (2022), 3. Edition p. 515–567, (ISBN 978-1-56990-806-8; E-Book: ISBN 978-1-56990-807-5; see AMK-Library under A 22) |
| [5] | Hoffmann, K.: Eine Einführung in die Technik des Messens mit Dehnungsmeß-streifen. Hottinger Baldwin Messtechnik GmbH, Darmstadt (1987); https://www.hbm.com/de/0112/fachbuch-eine-einfuehrung-in-die-technik-des-messens-mit-dehnungsmessstreifen/ |
Web-Link
Wikipedia–The Free Encyclopedia:Starin gauge: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Strain_gauge