Volume Resistance
| A service provided by |
|---|

|
| Polymer Service GmbH Merseburg |
| Tel.: +49 3461 30889-50 E-Mail: info@psm-merseburg.de Web: https://www.psm-merseburg.de |
| Our further education offers: https://www.psm-merseburg.de/weiterbildung |
| PSM on Wikipedia: https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polymer Service Merseburg |
Volume resistance
Definition of the volume resistance
The volume resistance is defined as the quotient of an electrical voltage applied between two electrodes and the current intensity measured between these electrodes.
Two ring-shaped plate electrodes are applied to the test specimen, which consists of a plastic or elastomer and whose contact surfaces must be flat and plane-parallel. However, other geometries are also possible (e.g. cylindrical electrodes). At a given voltage U, the value of which must be below the electrical strength in relation to the distance between the electrodes, and a constant current I, the resistance value is determined. The current along the surface is not taken into account, and possible polarisation phenomena at the electrodes are neglected.
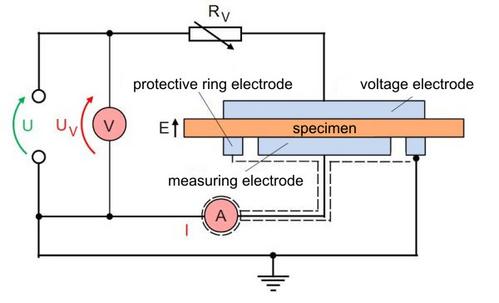
Measurement setup for determining the volume resistance
The volume resistance is determined according to the measuring set-up in Fig. 1. Here, U is the operating voltage and RV is a variable resistor with which the measuring voltage UV at the two electrodes of the measuring capacitor, in which the dielectric to be tested is located, can be set.
| Fig. 1: | Principle circuit diagram for measuring the volume resistance |
To prevent deformation of the electric field between the electrodes and to avoid the measurement errors caused by this, the anode (lower electrode in Fig. 1) is divided into a ring electrode, which is placed on the potential of the cathode, and a measuring electrode, with a gap of 5 mm between these two electrodes to prevent voltage flashovers according to DIN IEC 60093.
Typical plastics for testing the volume resistance are insulating materials such as polyethylene ( abbreviation: PE), polyvinyl chloride ( abbreviation: PVC), polyester ( abbreviation: PES), polytetraflourethylene ( abbreviation: PTFE or Teflon) and elastomers.
The electrical values of volume resistance and electrical strength are determined with a high-impedance resistance measuring device with connected measuring capacitor or with a electric strength tester.
See also
References
- Hellerich, W., Harsch, G., Haenle, S.: Werkstoffführer Kunststoffe: Eigenschaften, Prüfungen, Kennwerte. Carl Hanser Munich Vienna (2004) (ISBN 978-3-446-22559-6)
- DIN IEC 60093 (1993-12): Methods of Test for Insulating Materials for Electrical Purposes; Volume Resitivity and Surface Resistivity of Solid Electrical Insulating Materials (IEC 60093:1980), German Version HD 429 S1:1983 (withdrawn; replaced by DIN EN IEC 62631-3-1 (2023-10))
- DIN EN IEC 62631-3-1 (2023-10): Dielectric and Resistive Properties of Solid Insulating Matrials – Part 3-1: Determination of Resistive Properties (DC methods) – Volume Resistance and Volume Resistivity – General Method (identical with VDE 0307-3-1:2023-10)
- Schönhals, A.: Electrical and Dielectrical Properties. In: Grellmann, W., Seidler, S. (Eds.): Polymer Testing. Carl Hanser, Munich (2022) 3rd Edition, pp. 330–368 (ISBN 978-1-56990-806-8; see AMK-Library under A 22)
Additional References
- Dhakal, K. N., Lach, R., Grellmann, W., Krause, B., Piontek, J., Adhikari, R.: Piezoresitivity and strain-sensing behavior of poly (butylene adipate-co-terephthalate)/multiwalled carbon nanotube nanocomposites. Royal Society of Chemistry. RSC Advances (RSC Adv.) 14 (2024) 35715–35726 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/D4RA04826A