Melt Mass-Flow Rate
| A service provided by |
|---|

|
| Polymer Service GmbH Merseburg |
| Tel.: +49 3461 30889-50 E-Mail: info@psm-merseburg.de Web: https://www.psm-merseburg.de |
| Our further education offers: https://www.psm-merseburg.de/weiterbildung |
| PSM on Wikipedia: https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polymer Service Merseburg |
Melt mass-flow rate (MFR) (Author: Prof. Dr. H.-J. Radusch)
Measure of the MFR
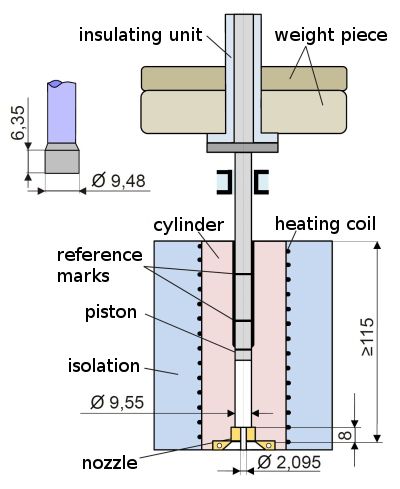
The melt index (MFR = Melt Mass-Flow Rate, the former MFI = Melt Flow Index) characterises the flow behaviour of a thermoplastic material. For measuring the MFR, melt index gauge systems, which are a special type of capillary rheometer (Fig. 1), are used to measure the melt index [1].
| Fig. 1: | Typical gauge system to measure the Melt index |
Melt mass-flow rate formula
The procedure for determining the melt flow index is standardised in ISO 1133 [2] and ASTM D 1238a [3]. The melt flow rate is defined as the MFR value, which indicates the amount of material in grams that flows through a capillary with defined dimensions in ten minutes at a certain pressure and temperature.
with
| m | average mass of the sections | |
| t | time interval for the cut-off | |
| tref | 600 s |
The melt flow index is given in the unit g (10 min)-1. The melt index value only represents a single value proportional to the viscosity at a relatively low shear rate. Due to the simple measuring principle, there is no direct comparability with viscosity values measured on high-pressure capillary rheometers.
Test conditions for measuring
The nozzle of the melt index tester is designed as a very short capillary, usually with an L/D ratio of 10/1. The pressure required to press the melt out of the temperature-controlled cylinder is realised by applying a defined load with support weights. The test conditions are specified in ISO 1133 [2]. Common test parameters for thermoplastics are summarised in the table. The respective test temperature is taken from the test standard, depending on the material and the load.
| Mass of the support weights (kg) | Piston force (N) | Piston pressure (bar) | Apparent shear stress (Pa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.325 | 3.187 | 0.4516 | 2.956 ⋅ 103 |
| 1.20 | 11.77 | 1.6670 | 1.092 ⋅ 104 |
| 2.16 | 21.18 | 3.0010 | 1.965 ⋅ 104 |
| 3.8 | 37.27 | 5.2800 | 3.457 ⋅ 104 |
| 5.0 | 49.03 | 6.9470 | 4.548 ⋅ 104 |
| 10.0 | 98.07 | 13.8900 | 9.096 ⋅ 104 |
| 15.0 | 147.1 | 20.8400 | 1.364 ⋅ 105 |
| 21.6 | 211.8 | 30.0100 | 1.965 ⋅ 105 |
The melt flow index MFR is frequently used in testing practice as a simple and quick method of incoming goods or quality control, but is also important in damage analysis or customer complaints.
Acknowledgement
The editors of the encyclopaedia would like to thank Prof. Dr. H.-J. Radusch, Martin-Luther-Universität Halle-Wittenberg and Polymer Service GmbH Merseburg for this guest article.
See also
- Melt volume-flow rate
- Moulding compound test
- Heat resistance
- Glowing hot-wire test
- Capillary rheometer
References
| [1] | Radusch, H.-J.: Determining Process-Related Properties. In: Grellmann, W., Seidler, S. (Eds.): Polymer Testing. Carl Hanser Munich (2022) 3rd. Edition, pp. 39–70, (ISBN 978-1-56990-806-8; E-Book ISBN 978-1-56990-807-5; see AMK-Library under A 22) |
| [2] | ISO 1133: Plastics – Determination of the Melt Mass-flow Rate (MFR) and Melt Volume-flow Rate (MVR) of Thermoplastics |
- Part 1 (2022-06): Standard Method
- Part 2 (2011-12): Method for Materials Sensitive to Time-temperature History and/or Moisture
| [3] | ASTM D 1238a (2023): Standard Test Method for Melt Flow Rates of Thermoplastics by Extrusion Plastometer
Weblink |
| [4] | Wikipedia – The Free Encyclopedia: Melt flow rate (MFR). https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Melt_flow_index |