ICIT – Extended Stop-Block Method
| A service provided by |
|---|

|
| Polymer Service GmbH Merseburg |
| Tel.: +49 3461 30889-50 E-Mail: info@psm-merseburg.de Web: https://www.psm-merseburg.de |
| Our further education offers: https://www.psm-merseburg.de/weiterbildung |
| PSM on Wikipedia: https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polymer Service Merseburg |
ICIT – Extended stop-block method
Stepwise crack length variation
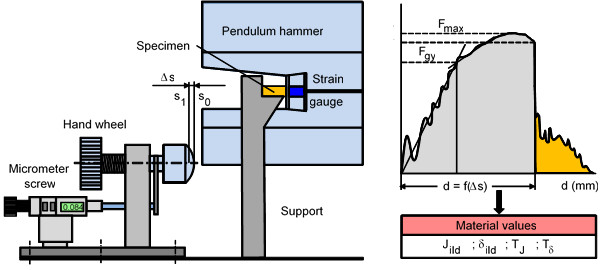
As part of the further development of the stop-block technique, a special test arrangement was designed that stops the hammer blade and no longer the hammer fin in the instrumented Charpy impact test and also compensates for the increasing skewness with decreasing Δa when the hammer strikes the test specimen (Fig. 1).
| Fig. 1: | Modified equipment for determination of crack resistance (R-) curves |
The stop-block method is carried out using deflection limiting elements of defined width increments or a catching device for the pendulum hammer (stop-block device) with defined adjustable (approved) test specimen deflections.
References
- Grellmann, W., Seidler, S., Oberbach, K.: Dynamische Risswiderstandskurven von Polymerblends. VDI-Berichte 882 „Experimentelle Mechanik in Forschung und Praxis, 14. Gesa-Symposium 25./26.04.1991 Berlin, proceedings pp. 433−443
- Grellmann, W., Seidler, S., Oberbach, K.: Ermittlung dynamischer Risswiderstandskurven von Polymerblends mit Hilfe des instrumentierten Kerbschlagbiegeversuches. 23. Vortragsveranstaltung, DVM- Arbeitskreis „Bruchvorgänge“ Berlin 26.-27.02.1991, proceedings pp. 401−412
- Savadori, A.; Bramuzzo, M.; Marega, C.: J. Integral Analysis of Ductile Fracture of PP/EP Rubber Blends. Polymer Testing 4 (1984) 73−89, https://doi.org/10.1016/0142-9418(84)90035-7
Continuous crack length variation
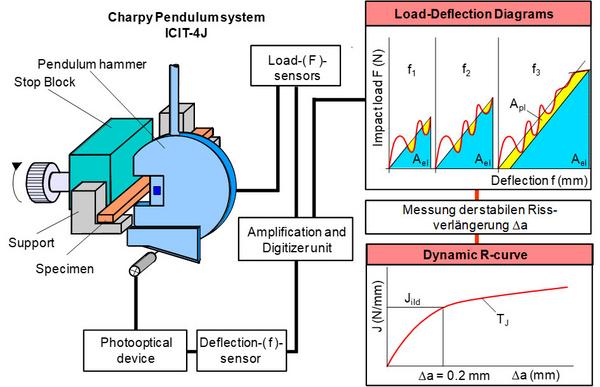
The stop-block method is carried out with the additional device shown in Fig. 2.
| Fig. 2: | Fracture mechanics workplace to carry out [MPK-Procedure MPK-ICIT |instrumented charpy impact test]] using stop-block equipment |
A continuous sequence of measurements from small to large crack extensions Δa or vice versa is useful; measurements are taken up to F ≤ Fmax of the previously recorded force–deflection diagram.
The force–deflection diagrams are recorded with the aid of the instrumented Charpy impact test (ICIT) under dynamic loading is explained in detail in the validated procedure of the testing laboratory "Mechanical Testing of Plastics": MPK-Procedure MPK-ICIT.
The final separation of the test specimens is carried out at low temperatures and/or high test speeds; the stable crack extensions Δa are then measured using a light microscope.
The dynamic modulus of elasticity Ed and the dynamic yield point σd are determined according to the equations known from the determination of crack toughness as resistance to unstable crack propagation.
See also
References
- Kobayashi, T.: Engng. Fracture Mechan. 23 (1983) 3, R 105–109 und 19 (1984) 1, R 49−65
- Server, W. L., Sheckherd, I. W., Wullaert, R. A.: CSNI-Spec. Meeting on Instrumented Precracked Charpy Testing, Palo Alto 1980
- Savadori, A., Marega, C., Bramuzzo, M.: J-Integral Analysis of Ductile Fracture of PP/EP Rubber Blends. Polymer Testing 4 (1984) 73−89