Gas Bubbles: Difference between revisions
Oluschinski (talk | contribs) Created page with "{{Language_sel|LANG=ger|ARTIKEL=Gasblasen}} {{PSM_Infobox}} <span style="font-size:1.2em;font-weight:bold;">Gas bubbles</span> __FORCETOC__ ==Criteria for the formation of gas bubbles== Gas bubbles can occur in plastic components both inside and on the edges of moulded parts (see: moulding compound). Due to the internal pressure that occurs, the surfaces of the gas bubbles are usually relatively smooth, in contras..." |
(No difference)
|
Latest revision as of 09:38, 2 December 2025
| A service provided by |
|---|

|
| Polymer Service GmbH Merseburg |
| Tel.: +49 3461 30889-50 E-Mail: info@psm-merseburg.de Web: https://www.psm-merseburg.de |
| Our further education offers: https://www.psm-merseburg.de/weiterbildung |
| PSM on Wikipedia: https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polymer Service Merseburg |
Gas bubbles
Criteria for the formation of gas bubbles
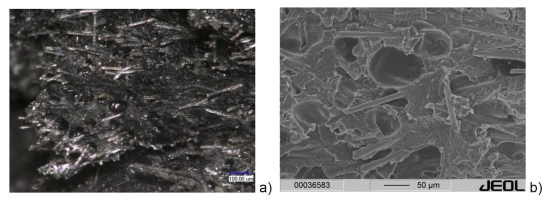
Gas bubbles can occur in plastic components both inside and on the edges of moulded parts (see: moulding compound). Due to the internal pressure that occurs, the surfaces of the gas bubbles are usually relatively smooth, in contrast to those of vacuoles (see Figure 1). The gas bubbles are usually round or oval in shape and elongated in the direction of flow. Gas bubbles are caused by trapped air, moisture (see: standard atmospheres) low-boiling substances or decomposition.
Gas bubbles form during processing, especially in hygroscopic materials such as polyamides (abbreviation: PA), if the material is damp or has not been sufficiently pre-dried.
Other causes of gas bubble formation can be thermal decomposition, excessive melt temperature, excessive residence time in the cylinder of the processing machine, or trapped air due to missing or insufficient degassing during processing.
| Fig. 1: | Gas bubbles in a component made of polyamide 66 with 35 M.-% glass fibres (PA66-GF35 |
See also
References
| [1] | VDI 3822 Blatt 2.1.2 (2024-06): Schadensanalyse – Schäden an thermoplastischen Kunststoffprodukten durch fehlerhafte Verarbeitung |
Additional references on polymer diagnostics/damage analysis
- Ehrenstein, G. W.: Kunststoff-Schadensanalyse – Methoden und Verfahren. Carl Hanser Munich, Vienna (1992) (ISBN 978-3-446-17329-3; see AMK-Library under D 2)
- Ehrenstein, G. W.: SEM of Plastics Failure – REM von Kunststoffschäden. Carl Hanser, Munich(2010) (ISBN 978-3-446-42242-1; see AMK-Library under D 5)
- Engel, D., Klingele, H., Ehrenstein, G. W., Schaper, H.: Rasterelektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen von Kunststoffschäden. Carl Hanser Munich, Vienna(1978) 1st Edition (ISBN 978-3-446-12560-5, see AMK-Library under D 8)
- Brostow, W., Corneliussen, R. D.: Failure of Plastics. Carl Hanser Munich, Vienna(1986) (ISBN 978-3-446-14199-5; see AMK-Library under D 10)
- Ezrin, Myer: Plastics Failure Guide – Cause and Prevention. Carl Hanser, Munich, 2nd Edition (2013) (ISBN 978-1-56990-449-7; see AMK-Library under D 7)
- Kurr, F.: Praxishandbuch der Qualitäts- und Schadensanalyse für Kunststoffe. Carl Hanser Munich (2014) (ISBN 978-3-446-43775-3; see AMK-Library under D 6-2)