HF-Scan: Difference between revisions
Oluschinski (talk | contribs) Created page with "{{Language_sel|LANG=ger|ARTIKEL=HF-Bild}} {{PSM_Infobox}} <span style="font-size:1.2em;font-weight:bold;">HF-scan </span> __FORCETOC__ ==Fundamentals== A simple imaging evaluation method for ultrasound testing is the HF-scan of an ultrasonic signal emitted by the measuring device itself ('''Figure'''). It corresponds to the movements of volume elements of the transducer in the time domain. Normally, the ultrasonic sensor ou..." |
(No difference)
|
Latest revision as of 09:50, 2 December 2025
| A service provided by |
|---|

|
| Polymer Service GmbH Merseburg |
| Tel.: +49 3461 30889-50 E-Mail: info@psm-merseburg.de Web: https://www.psm-merseburg.de |
| Our further education offers: https://www.psm-merseburg.de/weiterbildung |
| PSM on Wikipedia: https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polymer Service Merseburg |
HF-scan
Fundamentals
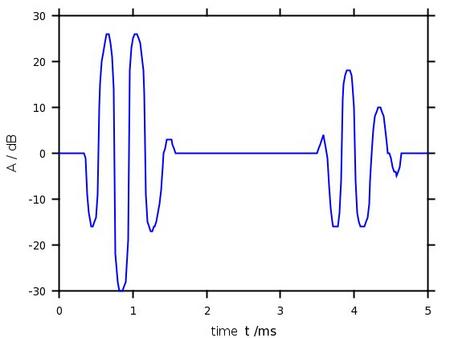
A simple imaging evaluation method for ultrasound testing is the HF-scan of an ultrasonic signal emitted by the measuring device itself (Figure). It corresponds to the movements of volume elements of the transducer in the time domain. Normally, the ultrasonic sensor outputs a voltage signal in units of volts, which is plotted over time. For better handling, the voltage signal is often scaled logarithmically.
| Figure: | Example of an HF-signal with logarithmic scaling from an ultrasonic measurement on aluminium with a wall thickness of 9 mm |
Practical relevance
The HF-scan can be used to determine the runtime and amplitude ratios. If the sound velocity is known, the wall thickness or fault depth can be determined. In principle, it is also possible to calculate the specific attenuation. Furthermore, signal filtering can be performed, allowing selective signal analysis. Signal filtering is based on Fourier analysis (see also: frequency analysis), whereby areas of no interest are cut out of the frequency spectrum. A reverse transformation is then performed, resulting in the filtered voltage signal, e.g. cleaned of interference or noise signals. This process is called signal convolution. If upper and lower frequencies are cut out, i.e. a high-pass and low-pass filter is applied, this is referred to as bandpass filtering.
See also
- A-scan technique
- B-scan technique
- Imaging ultrasonic testing
- C-scan technique
- D-scan technique
- F-scan technique
References
- Oberthür, W.: Basiswissen Elektrotechnik/Elektronik für nicht elektronische Berufe. Books on Demand GmbH, Norderstedt (2010) (ISBN 978-3-8391-9273-3)
- Deutsch, V.; Platte, M.; Vogt, M.: Ultraschallprüfung – Grundlagen und industrielle Anwendungen. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg (1997) (ISBN 3-540-62072-9
Weblink
- Wikipedia – The free encyclopedia: Radio frequency: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Radio_frequency